faintest of the brightest: grb hunters
Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs) are fascinating astronomical phenomena that have captured the attention of scientists and researchers around the world. These powerful bursts of gamma-ray radiation, lasting from a fraction of a second to a few minutes, provide valuable insights into the universe’s workings.
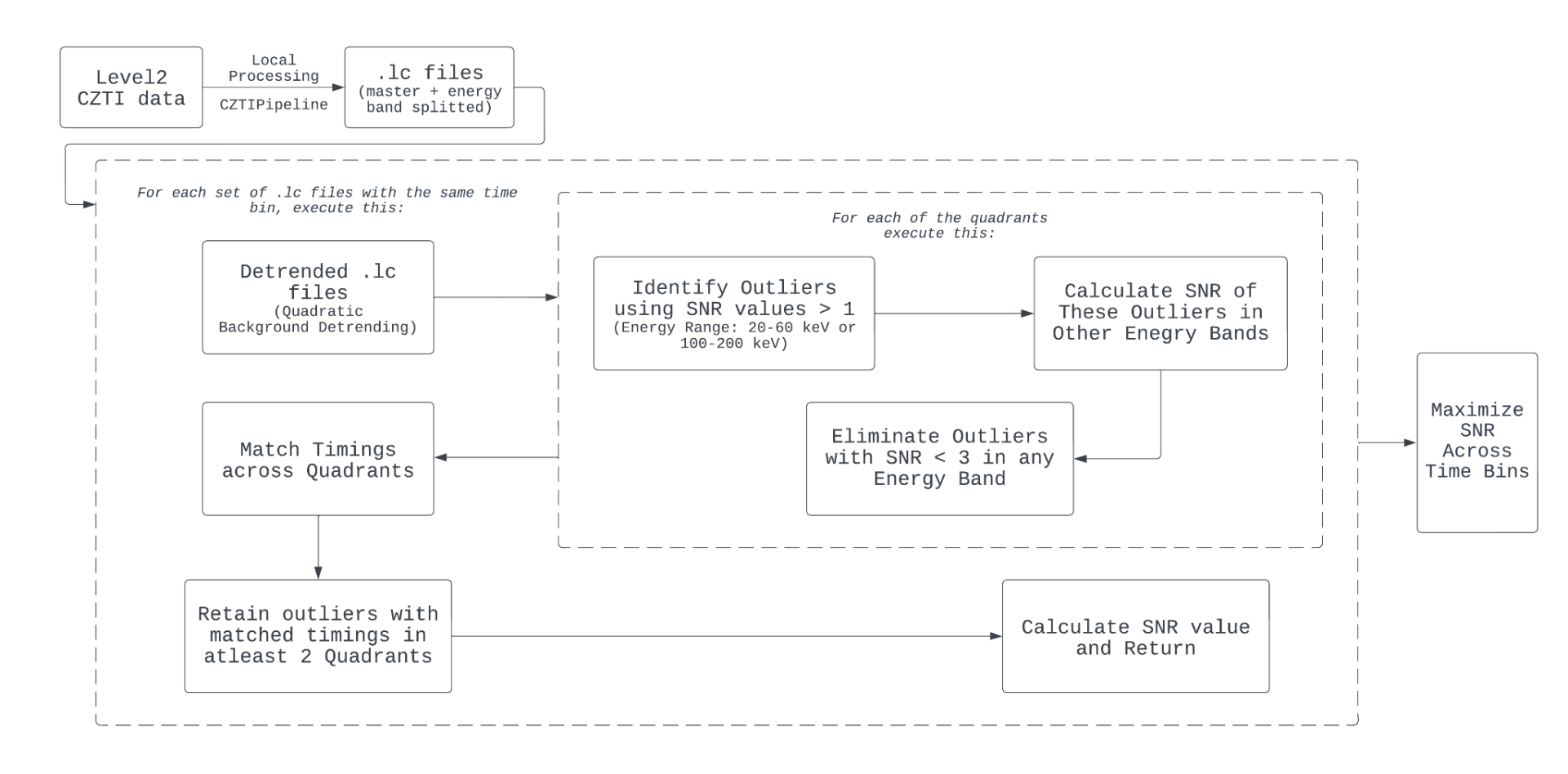
The implemented algorithm
The GRB Hunters project aims to create a method to detect grbs based on their signal-to-noise ratio in the data from the Cadmium Zinc Telluride Imager (CZTI) onboard ISRO’s AstroSat. By statistically analysing the noise in the data, a quantitative measure of the signal-to-noise ratio was obtained. This was then used to distinguish particle/noise data from real sources of gamma rays.
The logic was implemented in a python script that can be used to analyse the data from CZTI. On the left is the repository containing all the code developed for the project.